2Quality Assurance System
2.1 Quality Control in Manufacturing Processes
2.2 Control of Standards and Measuring Equipment
2.4 Customer Complaint Management
2.1 Quality Control in Manufacturing Processes
We consider that the quality control in manufacturing processes is most important to provide semiconductor products with the high quality and high reliability required by our customers.
For this purpose, we define the control conditions based on various technical information from our Engineering and Development Division in the Control Process Charts, document them, and conduct the individual manufacturing operations using them. The Control Process Charts mean the systematized process flows in which the equipment to be used, the materials to be used, individual quality control parameters, control standards, and inspection standards are described.
Semiconductor manufacturing consists of two main processes: the wafer process (front-end process) and the assembly process (back-end process). Below are example process flowcharts of our typical product.
_en.png)
_en.png)
2.2 Control of Standards and Measuring Equipment
1) Control of Standards
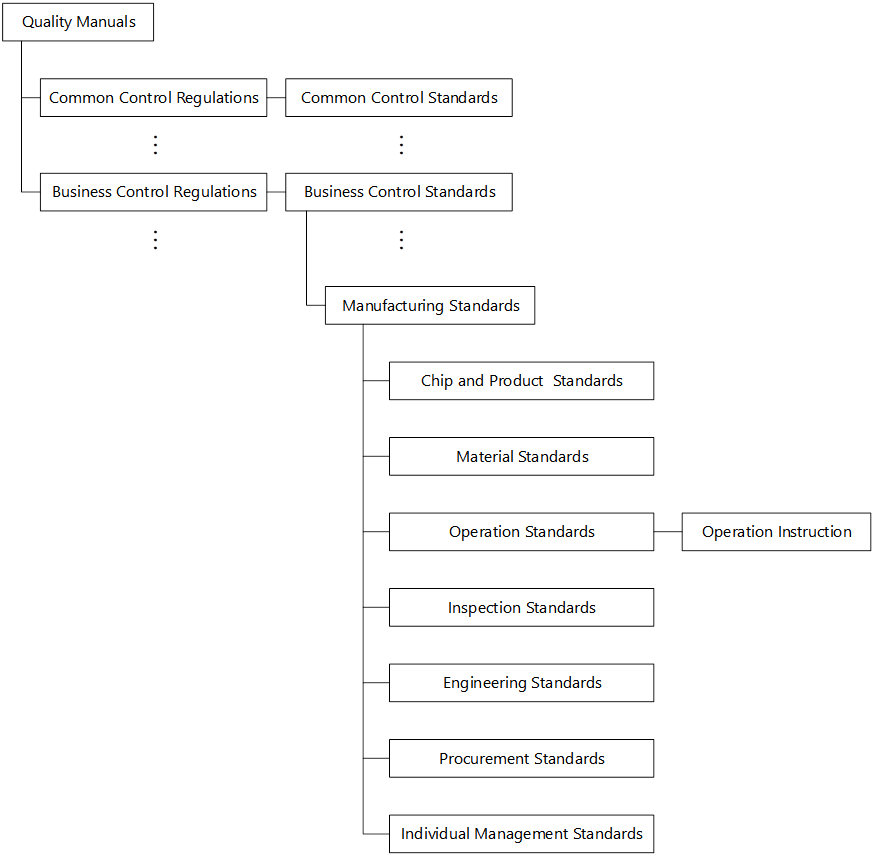
To maintain the quality and reliability of our products, we have established our product quality management system, i.e., the documented quality system where control regulations, control standards, and manufacturing standards and procedures are hierarchically organized with the quality manuals being at the top of the hierarchy. The above standards are instituted as systematized standards.
Below is the chart describing our standard system:
Standard System Chart
2) Control of Measuring Equipment
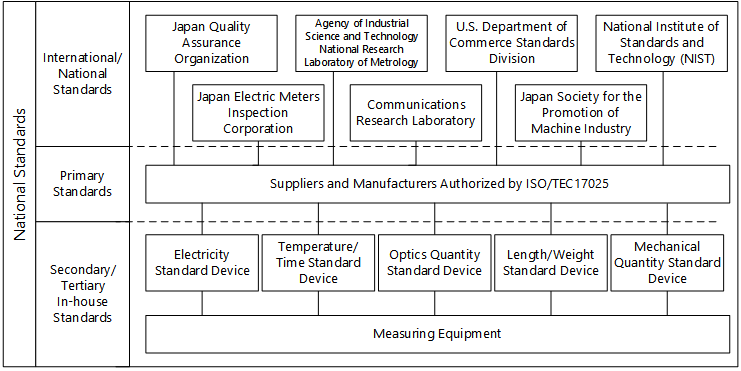
The qualities of the measuring equipment used for measuring electrical and optical characteristics of semiconductors can be ensured and improved by maintaining the equipment in a normal condition constantly and by allowing them to operate within the required accuracy levels. We have established the “Standards on Measuring Equipment Control and Operation” in our in-house regulations, which are confirmed that our traceability to the national standards is firmly established, and implemented regular inspections and calibrations at in-house or external calibration organizations.
Below is the chart showing our traceability system for the measuring equipment.
Traceability System Chart for Measuring Equipment
2.3 Product Traceability
We control the traceability of the products shipped to our customers so that their manufacturing histories can be traced by each marking on the product body, i.e., the part number and lot number.
Below is an example of the lot number marked on our product. For more details, please refer to the data sheet of each product. In addition, you can confirm the manufacturing history from packing conditions: the labels attached on shipping boxes also indicate the part numbers and lot numbers of the products being packed. (Please note that some products are excluded from this system.)
Example Marking of Lot Number
_en.png)
2.4 Customer Complaint Management
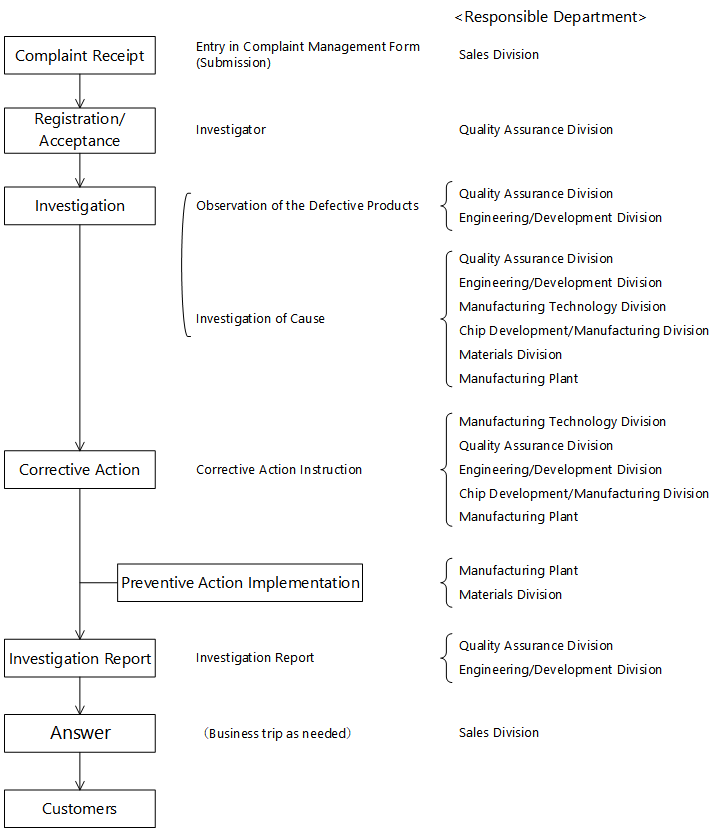
If any failure is found out from our products used in customer’s equipment, we will handle it according to the complaint management flowchart shown below.
Firstly, our Sales Division or authorized distributors will receive any complaints or returns from customers. The sales person who received a complaint then inputs its related information (incl. failure details, part number, user name, date received, set name, defect rate, lot) into the complaint management form of our electronic processing system, and informs our Quality Assurance Division of the complaint.
After that, the returned product is passed over to our Quality Assurance Division.
Based on the complaint management form, our Quality Assurance Division tries to grasp what state the failure is in and identify the cause from analytical investigation results on the returned product. According to the cause identified, they will determine what actions to take.
Subsequently, these analytical investigation results are fed back to our Engineering and Development Division and relevant manufacturing process operators on an as-needed basis. This is how we maintain and improve our reliability and how we attempt to prevent a reoccurrence of the failure.
We also report the progress of such investigation to the customer who sent the complaint as a “Complaint Investigation Report” through our Sales Division.
Complaint Management Flowchart
2.5 Quality and Reliability Education
We provide in-house education and training on quality and reliability to all the employees involved in work affecting quality, as our “Employee Training Implementation Standards” defines.
This system also allows the employees to actively participate in outside seminars, correspondence courses, and so on.
The table below shows our education and training courses, from basic to intermediate level, for general engineers.
In addition, we pre-train the operators involved in inspection and testing in the manufacturing processes before they are engaged to actual work on an as-needed basis. Those who have received the pre-training will work as qualified verifiers, contributing to the stabilization of our quality.
A person in charge of instructing and supervising checks the trainees’ comprehension levels as needed through their actual operations.
| Quality Education and Training Example | |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 Standard Requirements Explained | Statistical Method Practice 1 (Xbar-R Control Chart) |
| IATF 16949:2016 Standard Requirements Explained | Statistical Method Practice (P Control Chart) |
| PPAP Explained | Practical Problem Solving Method |
| Explanation of PPAP | Problem Solving Method |
| Value Engineering (VE) | Design (D) FMEA |
| Product Liability Law (PL Law ) | Process (P) FMEA |
| Basic: Problem Solving Method | Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) |
| Basic: Statistical Method | Quality Function Deployment (QFD) |
| Basic: Mistake and Error Proofing (Poka-Yoke) | Measurement System Analysis (MSA) |
| Basic: Customer Satisfaction | 5 Whys |
| Basic: 5S | |
2.6 Approaches to Quality-related Standards
1) Approach to ISO 9001 Quality Assurance Standard
ISO 9001 is an international standard for ‘quality assurance’ enacted by the International Organization for Standardization in 1987. Not the quality of a product itself but the quality management system is evaluated. In 2002, ISO 9001 was revised from the quality assurance standard to the ‘quality management system’ standard for managing organizations in terms of quality control. ISO 9001 aims not only to manufacture quality products but also to manage the system for creating (providing) quality products and services.
The term “quality products and services” means the products and service required by customers. More specifically, ISO 9001 encourages organizations to establish a system that will pursue customer satisfaction through providing the quality products and services.
2) Approach to IATF 16949 Automotive Quality Management Systems Standard
IATF 16949 is an international standard for quality management systems in which the automotive-specific requirements are added to the ISO 9001 standard. As ISO 9001:2015 was issued in 2015, our quality management system also migrated from ISO/TS 16949 to IATF 16949:2016.
_en.png)
Questions or Comments?
Please feel free to contact us if you cannot find the desired product from the lineup.
