IGBTs
What Is an IGBT?
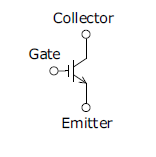
An IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) is a transistor whose input section has a MOS structure and its output section has a bipolar structure. This transistor has the characteristics of a MOSFET with high input impedance and high switching speed, and the characteristics of a bipolar transistor with low saturation voltage.
See IGBT Structure for the structure of the IGBT.
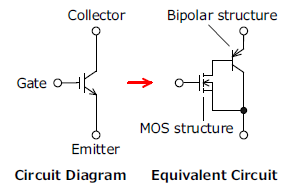
Features of IGBTs
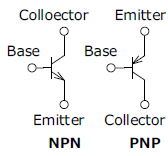
The features of IGBTs when compared with power MOSFETs and bipolar transistors are shown below.
| Item | Power MOSFET | Bipolar Transistor | IGBT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure (arrows indicate the direction of the drain current / collector current) | 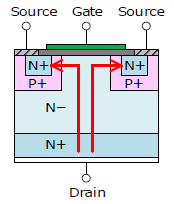 N-channel |
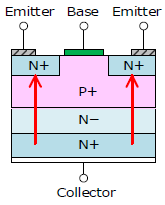 NPN |
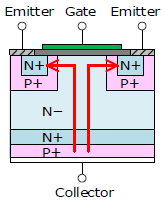 |
| Circuit Diagram | 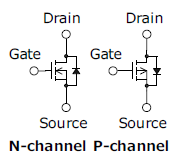 |
 |
 |
| Control Systems | Voltage control | Current control | Voltage control |
| Driving Power | Small | Large | Small |
| Switching Speed | Fast | Slow | Medium |
| Breakdown Voltage | About 30 V to 800 V | About 50 V to 800 V | About 400 V to 1200 V |
| Increasing the Current | Easy (about 1 A to 100 A) | Difficult (about 2 A to 25 A) | Easy (about 15 A to 40 A) |
| Applications |
|
|
|
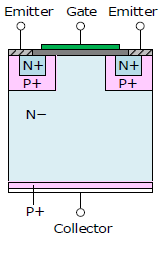
IGBT Structure
This section describes the structure and features of IGBTs. Compared to the punch-through type, the non-punch-through type and field-stop type have faster switching speed, lower loss, and thinner / smaller size.
| Structure | Punch-through (PT) Type | Non-punch-through (NPT) Type | Field-stop (FS) Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section View | 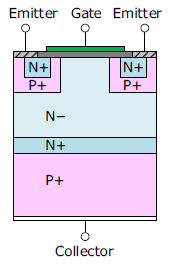 |
 |
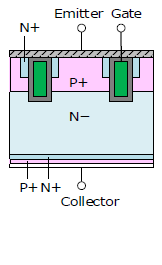 |
| Switching Speed | Slow | Fast | Fast |
| Short Circuit Withstand Time | Short | Long | Medium |
| Manufacturing Difficulty | Easy | Difficult | Difficult |
Questions or Comments?
Please feel free to contact us if you cannot find the desired product from the lineup.
